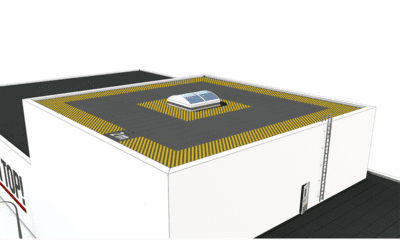
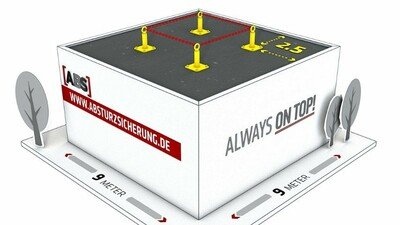
Fall danger zone close to the edge of a structure
A fall danger zone is any area where a access or work route comes within 2 m of the edge of a structure. It is mandatory to provide a fall arrest solution for all employees working within this zone. The edge may be the edge of a roof but could also be the edge of a domed rooflight or a smoke and heat extraction system. In accordance with DIN 4426, an access route on a roof surface must be accordingly secured as soon as the potential fall distance exceeds 1 meter, in as far as this access route is located within a fall danger zone. If the roof pitch is greater than 20 degrees, care should be taken to ensure that a permanent fall arrest system is installed. Please find below a list of the most important provisions dealing with the topic of fall arrest and rope protection:
- ASR A2.1 “Protection against falls and falling objects, entering hazardous areas”
- DGUV Principle 312-906 “Selection, training and certification of specialists for personal fall protection equipment”
- DGUV Publication 201-056 “Basic planning guidelines for anchorage devices on roofs”
- DGUV Rule 112-198 “The use of personal fall protection equipment”
- DIN 4426 “Equipment for building maintenance - safety requirements for workplaces and accesses - design and execution"